If you are looking for the answer to “why is UVA light considered a mutagen?”, obviously, you are here at the right place. After reading this post, all of your doubts will be cleared.
The sunlight’s ultraviolet radiation is called UV light. It is vital for vitamin D making, but it can be particularly harmful to the eyes and skin. Furthermore, that is the reason why UVA light is considered a Mutagen.
In addition to the threat of vision loss and premature skin aging, the cancer risk that the rays bring with them is feared. Only about 10 % of the sun’s UVB radiation reaches the earth.
In regions like the South Pole, the ozone layer is thinned or no more available, the values of UVB are consequently increased massively.
UVA rays, on the other hand, are not even intercepted by the atmosphere. They almost wholly reach the surface of the earth.
What is UVA Light?
The sun’s rays reach on earth in various electromagnetic wavelengths: such as ultraviolet light, visible light, and infrared light.
Rays that the human eyes can observe are summarized in the range of noticeable light; infrared light can be felt as heat. In contrast, humans cannot see the light from the UV range.
UV wavelengths and their properties
Ultraviolet light is divided into the UV ranges A, B, and C based on its wavelength:
-
- UVA light: 400 to 315 nanometers
- UVB light: 315 to 280 nanometers
- UVC light: 280 to 100 nanometers
UVC radiation catches nitrogen, ozone, and other different types of gases in the atmosphere since the ray has a germicidal effect, artificially and using, for example, for disinfection.
What is Mutagen?
The Mutagens are substances that can trigger mutations in the genome of organisms. These substances include a variety of chemicals (e.g., formaldehyde, mustard gas) and physical influences.
Physical influences are, e.g., UV light and radioactive radiation. The extent to which environmental influences (e.g., climatic factors, industrial emissions) can trigger changes in the genome depends above all on the inexactly measurable increase in the mutation rate compared to the natural rate.
However, these are substances that can trigger mutations in the genome of organisms. They include a variety of chemicals (e.g., formaldehyde, mustard gas) and physical effects.
Why is UVA light Considered a Mutagen
UV light and radioactive radiation. The extent to which environmental influences (e.g., climatic factors, industrial emissions) can trigger changes in the genome depends above all on the inexactly measurable increase in the mutation rate compared to the natural rate.
Overview of Mutagens and their Effects
The chemical substances that can trigger genetic material changes include tar substances, base analogs, nitrous acid, and acridine dyes. Tar substances in tobacco products are carcinogenic.
Besides, they have a molecule with a ring system and slide between the nucleotides. Therefore, they are faking one base too many.
When the DNA replicates, any other base is attached to this simulated base. This DNA strand is longer by one nucleotide.
Bromacil – A Base analog
Bromacil is one of the so-called base analogs. In terms of their chemical structure, these substances have a certain similarity to the expected bases of DNA and can therefore represent them and even form a base pair.
Since, Bromacil is similar in structure to the purine and pyrimidine bases. During replicating the DNA, the thymine is replaced by the bromouracil so that the base-pairing adenine-bromouracil is now present.
However, it is an unstable base. This can lead to a pairing of the bromouracil with guanine instead of the complementary adenine due to a hydrogen atom’s rearrangement.
After replication, the A-T base pair of the DNA becomes a G-C base pair. If the DNA replicates after such a change, a mutation can result.
Nitrous Acid Changes Cytosine (deamination) in Dormant DNA
This converts cytosine into uracil. This uracil is no longer complementary to guanine but adenine. If the DNA replicates, the base pair C-G in the double-strand is replaced by the base pair U-A.
This results in replication errors. Errors can occur during the reading process. This renders a protein ineffective. Acridine dyes can slide between the nucleotides of the DNA and thereby change their base sequence.
The physical influences that can trigger the genome’s changes include high-energy rays, e.g., B. UV rays, radioactive rays, and X-rays.
Short-wave UV Rays
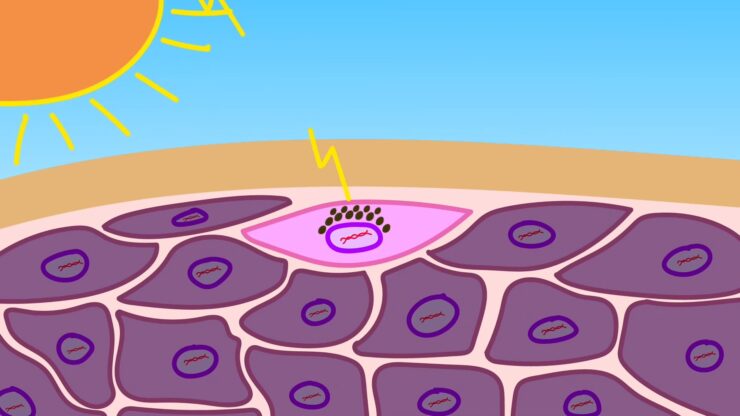
Short-wave UV rays (e.g., solar and cosmic rays) link neighboring thymine bases of a DNA strand (thymine dimers). These can then not pair with the complementary bases adenine. The genetic information can no longer be read precisely at these points.
Radioactive radiation and X-rays do not act directly on DNA. However, they form very reactive radicals in the cells, which then enter into chemical reactions with the DNA.
This can lead to breaks in the double or single element of DNA. The consequence can be a base exchange or the failure of a nucleotide within the DNA.
It is very dangerous for the organism if radioactive substances get into the body through food and remain there for a long time.
How does UVA Light Affect Mutagen
Besides, there are lots of worthy reason why is UVA light considered a mutagen. Generally, we see the Ultraviolet rays from the violet end onwards, opposite to the red end.
Hence, it is a shorter wave; the higher the electromagnetic frequency, it also corresponds to higher energy.
Combination of Electromagnetic Frequency & Higher Energy:
Combining both characteristics, a more incredible penetrability is also obtained in Organic compounds. Therefore, the material that makes up living beings can affect molecular bonds in a more or less significant way in proteins.
Transcription Mechanism
But when this effect occurs in the molecule of the material contained in the cell nucleus, it can be sufficient for the transcription mechanisms to deliver a slightly different sequence in the target protein formulation.
Creates mRNA Chain
As we can assume, it is such a change can be temporarily harmful if it happens in the mRNA chain. Also, it can later be replaced with more correct copies, but the modification occurs directly in the nuclear material.
Cancer is a mutation, which occurs when healthy cells receive an external stimulus; as well as, it becomes diseased cells, leading to metastasis and dying slowly and painfully.
Hence the personal care campaigns for people who enjoy summer on the beach and in the mountains and put sunscreen on any skin exposed by clothing.
A UV Index reading of 3-5 means a moderate hazard of damage from insecure sun exposure. Stay in the shade around noon when the sun is strongest. If you are outdoors, wear clothing that protects, a wide-teemed hat, and sunglasses that blocks UV rays.
Is It Good or Bad
While we are talking about why is UVA light considered a mutagen, we also need to have the proper knowledge about it’s affects on our planet. Diverse ranges of UV lights have altered physical properties and also have dissimilar effects on the creature.
The body has various repair mechanisms that minimize damage from UVB and UVA radiation. However, if you repeatedly expose yourself to the sun unprotected or for too long, self-protection is no longer sufficient.
Moreover, the moderately long-wave UVA lights penetrate to the derma. Therefore, it hazards the collagen structure and can produce free radicals that can cause the feared blacked skin cancer in particular.
The UVB light in the center field penetrates less deeply. It is necessary for Vitamin D formation. Conversely, it reasons sunburn and can debase the skin cells in the basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
The most substantial harm caused by Ultra Violet light at a glance:
-
- Skin cancer precursors
- Sunburn
- Sun allergy
- Permanent over pigmentation (liver spots, age spots)
- Breakdown of collagen in connexion tissues: premature aging and skin wrinkles, dermis
- Conjunctivitis of the eye, Corneal inflammation
- Damage to the eye’s retina and lens
- Brittle and dry hair that is tough to comb
- Other various types of skin cancer
Conclusion
The level to which Ultra Violet light is injurious depends not only on the type of skin but also on various environmental factors. That also depends on you are from which part of the world; solar radiation is stronger or weaker.
Now, we can say that you have got the answer to why is UVA light considered a mutagen? The danger is exceptionally high in the mountains because of the cleaner and thinner air.
However, it becomes hazardous in winter sports because the snow imitates approx. 80% of the Ultra Violet light. The nearer your location to the equator, the more intense the UV light is.
Alternately, The viewpoint at which the radioactivity hits the skin is particularly steep here. Even the beach’s light sand reflects around 25% of the radiation.
Eventually, you are not safe underwater either: even 1/2 a metered surface’s below, Ultra Violet light capable of reduce only by 60%. Dense cloud covers can, as a minimum, moderately reduce the rays.
However, skin damage or sunburn is also possible when the sky is cloudy.